QR Code Payments – Just Another Contactless Payment Method?

Cutting expenses and streamlining processes stand as the primary motivations for embracing digital transformation. When these elements merge and technology becomes user-friendly and accessible to all, it has the potential to significantly reshape our approach to mundane daily tasks. An example of such a clever solution is the creation of the QR code.
The financial services sector has acknowledged the potential embedded within the two-dimensional code. Consider the familiar frustrations associated with executing transactions using seemingly endless account numbers or IBANs, often resulting in denied transactions due to inadvertent errors in digit placement. Imagine the convenience of delegating the task of inputting these transaction details to someone or something else. Herein lies the efficacy of a QR code.
In this blog post, we discover what a QR code is and how it works, and we explore its potential in facilitating smoother, more streamlined and more convenient money transfers. We also examine how it can be integrated into an established system and existing frameworks, and conclude by highlighting SEEBURGER’s role in facilitating payments integration.
What is a QR code and how does it work?
Before diving deeper into QR code payments, let’s have a look at what QR codes actually are and how they work.
QR is short for “quick response” and these codes contain information in a matrix-like pattern of black squares on a white background. They have gained widespread popularity due to their ability to store and share various types of data, including contact information, URLs, texts and images, among others, which facilitates interactions between the physical and digital worlds. Their versatility and ease of use have led to their widespread adoption in various fields, including marketing, ticketing, inventory management, and of course, payments.
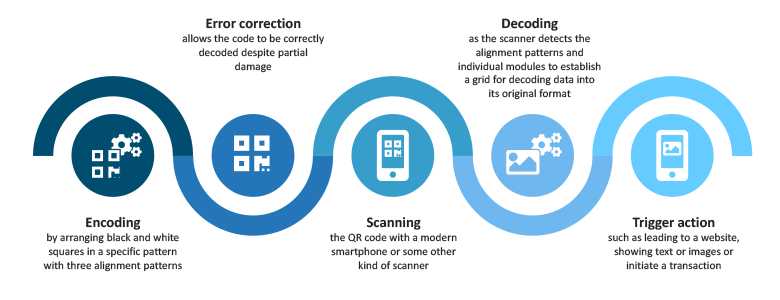
To be able to store and share data, the functioning of a QR code involves a few key principles:
- QR codes encode information by arranging black and white squares in a specific pattern. Each square represents a binary digit (bit), with patterns being read both horizontally and vertically. QR codes use a process called data masking to further enhance reliability. This involves applying a specific pattern to the modules to ensure a more balanced distribution of black and white modules. When encoding, special patterns are added to the QR code to assist with accurate scanning. These include three large square markers called alignment patterns that help scanners adjust for any rotation or distortion, as well as timing patterns that define the size and position of the modules.
- QR codes incorporate error correction. These codes allow the QR code to be partially damaged or obscured and still be correctly decoded later on. Most commonly, QR codes use Reed-Solomon error correction, which can recover data even if a certain percentage of the code is damaged.
- To decode a QR code, you need a QR code scanner. Usually, smartphones come equipped with built-in QR code scanners through their camera apps. The decoding process actually looks like the encoding process in reverse. The scanner captures the image of the QR code and identifies the alignment patterns to determine orientation and size. The scanner then detects individual modules and establishes a grid that divides the QR code into cells. The scanner decodes the encoded data based on the specific data-encoding mode used in the QR code and converts the binary data back into the original data format, which could be a URL, text, contact information or other types of data.
- Depending on the decoded data, the QR code can trigger various actions. For instance, if the QR code contains a website URL, scanning it might open the website in the user’s web browser. Similarly, if it contains contact information, it can prompt the user to save the contact details. Or, if it contains bank account details, it can initiate a transaction within a banking app on the device.
What exactly are QR code payments?
QR code payments refer to a method of conducting financial transactions using QR codes as the medium of exchange. QR code payments have emerged as a convenient method of conducting financial transactions in today’s digital landscape, as this innovative approach streamlines the payment process with efficiency and ease. By utilizing a mobile app or a QR code scanner, individuals and businesses can initiate transactions by simply scanning a QR code displayed at the point of sale, on invoices or within payment requests. This serves as a substitute for executing electronic fund transfers during a point-of-sale transaction that uses a payment terminal and payment methods like cash, credit cards or bank transfers.
QR code transactions, when it comes to digital payment methods, gained popularity due to their convenience, speed and security, and countries like Singapore and Indonesia are set to introduce QR code payments¹ for cross-border payments between the two countries. Singapore has notably taken a leading role in this domain. As early as 2018, it introduced what it asserted as the globe’s pioneer unified payments QR code. Following this milestone, Singapore subsequently conducted a cross-border pilot alongside Malaysia, while Indonesia and Thailand have similarly interconnected their respective systems.
To return to answering the question from the headline – are QR code transactions just another contactless digital payment method? — QR code payments distinguish themselves from other digital payment methods through their unique characteristics and operational approach. While other digital payment methods exist, QR code payments offer distinct advantages that set them apart:
- Simplicity and accessibility: QR code payments are exceptionally straightforward for both consumers and merchants. Anyone with a smartphone can use QR codes, making it an inclusive and accessible option. In contrast, other digital payment methods may require specialized hardware and software. In that sense, QR code payments typically don’t require extensive infrastructure or costly equipment but use simple technology instead, making them a cost-effective solution, especially for small businesses.
- Speed and convenience: QR code transactions are incredibly swift. Customers can scan a QR code and complete a payment within seconds, enhancing the overall checkout experience. Other digital payment methods, such as bank transfers or some mobile wallets, might involve more steps and take longer to process.
- Cross-border transactions: Having mentioned the example of Singapore and Indonesia, QR code payments have demonstrated their potential for cross-border transactions, enabling seamless payments between countries and reducing the complexities associated with international fund transfers.
Traditionally, cross-border transactions have been accompanied by complexities such as currency conversion, varying payment methods and lengthy processing times. QR code payments offer a solution to these challenges by providing a standardized and user-friendly platform for conducting transactions across different countries and currencies. - Standardization and interoperability: QR codes can be standardized across different payment platforms and systems, promoting interoperability. This standardized approach fosters collaboration among various stakeholders, including banks, payment providers and merchants, even across national borders as just mentioned above.
- Offline transactions: In certain scenarios, QR code payments can be processed offline, allowing for transactions even when there is limited or no internet connectivity. This can be beneficial in areas with unreliable network coverage. QR codes can do so by leveraging their inherent data storage capabilities and incorporating specific features designed for offline scenarios. Besides the data storage, offline QR code transactions can also rely on authentication methods that do not require an internet connection, the merchants’ device storage, peer-to-peer connectivity, and physical cards.
While QR code payments offer numerous benefits, it is important to note that they might not replace all other digital payment methods entirely. The choice of payment method depends on factors such as user preferences, merchant capabilities and the specific context of the transaction. However, QR code payments have clearly carved a distinct niche in the digital payment landscape, offering a compelling alternative that is gaining momentum on a global scale.
QR code payments integration
Having explored all the benefits of QR code payments, you may want to use these as a merchant if you have an existing payments landscape with well-running systems. Let’s explore how you can combine these two and integrate QR code transactions into your payments landscape while ensuring a seamless and effective implementation:
- API integration: QR code payment providers often offer APIs that allow you to connect their payment functionality with your existing systems. Create an account with the chosen payment provider and obtain the necessary API credentials, such as API keys or tokens. These credentials will be used to authenticate and authorize your API requests. Thoroughly review the API documentation provided and understand the endpoints, request parameters, response formats and authentication methods.
- Testing: Most payment providers offer a sandbox or test environment where you can experiment with the API without processing real transactions. Set up a test environment and work with your development team to incorporate the QR code payment API into your application. Use programming languages and tools compatible with the API.
- Error handling and security: Utilize the API endpoints provided by the payment provider to generate QR codes dynamically, including payment details, such as amount and recipient information. Implement logic to handle API callbacks and responses. This ensures that your application can process payment confirmations, errors and other relevant notifications from the payment provider. Equally important are security measures. Consider encryption and secure authentication to protect sensitive data transmitted between your application and the payment provider’s API.
- Monitoring and maintenance: When you are confident in the integration’s stability and functionality, deploy the QR code payment feature to your live environment. Monitor its performance, user adoption and any potential issues. Stay updated with the payment provider’s API updates and implement necessary changes or improvements to your integration as needed.
By following these steps and closely following the API documentation provided by the QR code payment provider, you can successfully integrate QR code payments into your existing systems and enhance the payment experience for your users.
How SEEBURGER can help with payment integration
The SEEBURGER Payments Integration Hub enables your payments infrastructure to work with your existing applications, while offering configurable workflows and integration capabilities into AML and backend applications. The SEEBURGER Payments Integration Hub, powered by the secure and scalable SEEBURGER BIS Platform, handles data conversions, compliance and backend integration for automated accounts payable and receivable, automatic reconciliation and faster straight-through processing.
The BIS Platform and its integration capabilities support financial service providers with digitalization initiatives such as payment modernization, real-time and instant payment functions, compliance management and cloud migrations. Take the burden off customer onboarding, secure and managed data transfer and the administration of numerous different payment formats with our Payments Integration Hub so that you can focus on your core business.
Webcast On-Demand
Learn more about creating an agile payment ecosystem in this webcast on demand.
Watch now¹ https://www.finextra.com/newsarticle/42805/indonesia-and-singapore-set-to-introduce-qr-code-payments
Thank you for your message
We appreciate your interest in SEEBURGER
Get in contact with us:
Please enter details about your project in the message section so we can direct your inquiry to the right consultant.
Written by: Sandrine Wagner
Sandrine joined our marketing team in August 2021 as an editor and campaign manager. She holds a Bachelor's degree in International Business and brings fundamental expertise in FSI and FinTech to our marketing team through her network engagements, previous internships and student jobs. After her internship at SEEBURGER, she joined our editorial team full-time and has since been involved in writing creative and technical content for our blog and other resources in German and English. Her campaign management work focuses on trends and innovations in various sectors, most notably the financial industry. In her free time, Sandrine enjoys exploring nature with her pets, learning foreign languages and reading literature.





