EDI invoice: What does EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) mean for E-Invoicing?

In order to understand the importance of EDI procedures for e-invoicing, it is very helpful to possess the knowledge gained in half a century of EDI practice. As early as the seventies, large companies and their partners in the business-to-business sector began to use EDI message standards and communication protocols to exchange and automatically process large quantities of electronic data quickly, securely and efficiently.
SEEBURGER has played an active and decisive role in shaping the current EDI practice. As an EDI pioneer, we have been supporting our customers worldwide since the early eighties in the implementation and integration of all processes related to EDI invoicing, i.e. e-invoicing and e-ordering.
EDI Invoice: Development of EDI E-Invoicing
EDI has long focused on the processing of documents such as purchase orders, order confirmations and shipping notifications as part of direct material procurement within the physical supply chain.
The financial supply chain, in turn, consists of invoices and credit notes, among other things, and ultimately ensures the settlement of accounts and payments with the supplier. However, the financial supply chain in particular has been a relatively low priority for many companies when implementing EDI e-invoicing. Thus, although EDI purchase orders and EDI despatch advices were received by the supplier, invoices and credit notes were still sent to the customer in paper form and not as e-invoices.
Only large companies, such as automotive and retail groups that have to handle a very large number of invoices and credit notes every day, paid close attention to the use of EDI for e-invoicing in order to save process costs. Many medium-sized companies had great uncertainties as to the extent to which EDI e-invoicing could be suitable for tax-compliant electronic invoicing. But was this, and is this uncertainty justified?
Which aspects have to be considered for legally compliant electronic invoices?
When it comes to e-invoicing, each country has numerous different tax law requirements. Knowing these specific requirements for e-invoicing in each country is a complex task. It is easy to risk being fined or failing to claim the input tax deduction. Even when invoices were still being sent in paper form, it was a challenge for multinational companies to keep track of them. However, electronic invoicing has by no means reduced this complexity due to the lack of transnational standards and regulations – much to the regret of the companies. For example, how long have legally required electronic signatures inhibited the spread of electronic invoicing? Also the requirements for electronic archiving and new procedures for real-time monitoring and control of invoice transactions by the tax authorities of the federal states themselves have not exactly contributed to a simplification of the processes.

EDI Invoice Benefits: Use EDI invoices to meet the requirements of the tax law and other relevant laws
EDI invoices support compliance with local legal requirements in many countries:
- Business partners’ agreement to e-invoicing: The business partners agree in writing via an EDI contract in which e-invoicing format (XML, EDIFACT) and via which transmission methods (directly via AS/2, or indirectly via so-called Value-Added-Network-Provider (VAN-Provider), such as the Peppol network) invoices should be exchanged.
- Integrity and authenticity: Using secure EDI transmission methods, the identity of the invoice issuer and the integrity of the content can be verified clearly and securely.
- Verification of the invoice contents: The invoice contents of e-invoices must be checked for correctness and compliance with legal requirements in the same way as classic paper invoices, which is automated and cost-efficient when using EDI invoices.
- Archiving the e-invoices: The archiving of electronic invoices must take into account the minimum storage period applicable in each case, in addition to other aspects such as immutability, access, human readable presentation, support for an audit process, etc. EDI invoices are automatically transferred to an electronic archive in accordance with country-specific legal regulations, in a package with relevant objects.
- Machine readability and data access: Machine readability is possible via the agreed message standard and EDI integration solutions. Data access by the tax authorities must be ensured without restriction, for which purpose special roles and authorizations can be used within the ERP and archiving system.
Given that EDI invoices have the potential to be genuine e-invoices and also offer the advantages of fast, mass invoice exchange at low transaction costs, why haven’t EDI invoices long since reached the winners’ rostrum?
The reasons for this include the following:
- A fast RoI is often only possible with a high number of transactions between two partners. This is because the costs for the EDI connection are offset by the savings in process costs through electronic mass data exchange and automated further processing.
- Industries vary in EDI capability. Industries in which many suppliers work with many customers use less EDI e-invoicing compared to the automotive industry and trade, where the few large companies were able to ‘convince’ their partners of the use of EDI for e-invoicing more easily.
- The main beneficiary of EDI e-invoicing is the customer: suppliers can create PDF invoices and send them to many customers at very low cost, whereas EDI e-invoices initially incur higher implementation costs. For customers on the other hand, incoming invoices in PDF format mean higher processing costs due to manual invoice entry, correction and processing. These in turn are largely omitted with EDI e-invoicing.
EDI Invoice Example: Have countries already managed to solve the balancing act between ‘PDF simplicity’ and ‘EDI efficiency’?
The answer is ‘yes’. In Europe, the Scandinavian countries (with Norway as the primary example) have achieved this goal first and foremostly. Italy has also successfully implemented e-invoicing – albeit in very different ways.
E-invoicing is now very widespread in Scandinavia – and by far not only between large, high-transaction business partners, but even among micro-enterprises. Here, e-invoicing providers (VANs) with interconnections to other e-invoicing providers help to connect all suppliers and customers of these providers simply as required via a four-corner model.
Italy has legally introduced the obligation for e-invoicing and in this way has processed over 2 billion electronic XML invoices in 2019 via the state Sistema die Interscambio (SDI). Here too, one usually works with e-invoicing providers that are connected to the SDI in order to exchange outgoing and incoming invoices with business partners.
Summary
- EDI e-invoices can meet legal requirements in many countries around the world
- Security, integrity, authenticity and legally compliant electronic archiving must be ensured
- The type of invoice exchange depends, inter alia, on national laws, B2B practice, industry standards and the cost-benefit aspects of the business partners
- Successful global EDI e-invoicing includes direct partner connections as well as indirect partner connections via Peppol or EDI/E-invoicing VAN providers
With the SEEBURGER Cloud Services we offer you a plug-and-play cloud service for EDI messages, Peppol, and VAN communication, through which you can exchange e-invoices, e-orders and other documents. This scalable and future-proof service comes from a single source, from an experienced cloud partner who understands and can meet the diverse requirements of different countries, industries and business partners. In this way, you avoid the disadvantageous, cost- and complexity-increasing orchestration of many local providers.
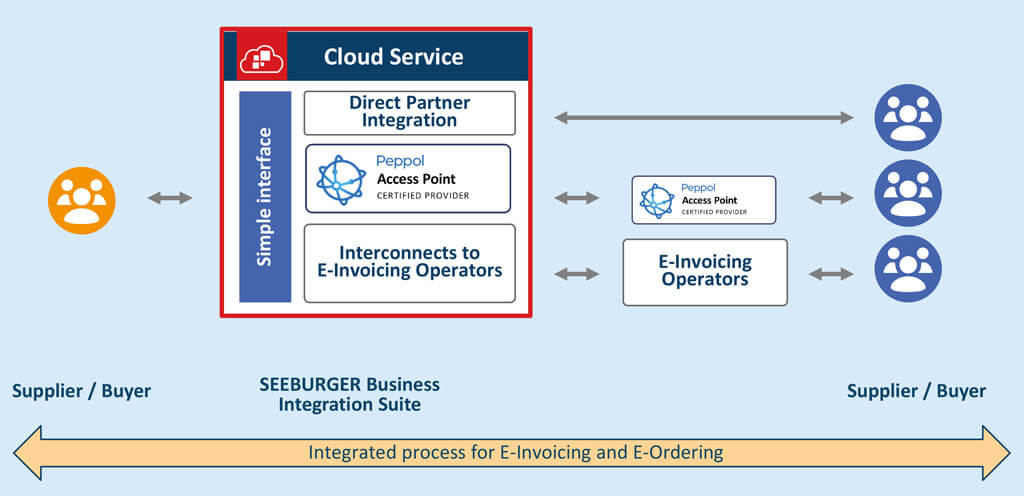
With the SEEBURGER cloud services for EDI e-invoicing and e-ordering, you can directly or indirectly exchange EDI e-invoices and other procurement documents with your business partners and meet the legal requirements. Our services can be used independently of ERP systems.
Furthermore, there are options to use the SEEBURGER Business Integration Suite as an in-house operation on site or as an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS).
Thank you for your message
We appreciate your interest in SEEBURGER
Get in contact with us:
Please enter details about your project in the message section so we can direct your inquiry to the right consultant.
Written by: Gerrit Onken
Gerrit Onken has been at SEEBURGER since 2010 as a product manager for software applications and for electronic data exchange services for the business sector. He focuses on solutions for SAP, electronic invoicing (e-invoicing) and innovations for digitalizing business and technical processes for globally-active customers. Originally a banker, Gerrit Onken went on to graduate in business administration, majoring in industrial management and business informatics. After working in the financial sector, he worked as a manager and project manager from 2004 to 2010 for one of the top five corporate consultancies, working with international BPOs in the banking and automotive industries.





