Crypto Currencies: How Blockchain is Revolutionizing the Banking System

Since the dawn of commerce, our financial system and the way we pay for goods and services have been constantly evolving, always with three goals: faster, more convenient and safer. First, we exchanged everyday objects, then we traded gold and silver and then we settled promissory notes. With the introduction of cashless and contactless payments, even our current cash system is almost out of fashion again. As the “means of exchange” continues to change, does this mean that in the near future, all of our payments will be digital or virtual? Are crypto currencies on the verge of a huge financial revolution, or is it just pure speculation that will end as quickly as it began?
Digital currencies have been around for quite some time — since 2008 to be precise, when the banking crash changed a lot. Today, there are already over 9,000 crypto currencies in circulation and they promise immense growth. The best known of these, according to a study by Statista dated April 21, 2023, are Bitcoin, Ripple and Ethereum. But does “new” and “digital” automatically mean better and safer?
The euro, dollar and yen are globally strong and stable currencies whose cash is frequently used for payments in everyday life. Value is ascribed to money in this context, because the material of a $20 bill is, of course, not directly worth $20. While this value used to be tied to the value of gold, today, banks and states ensure that their currencies retain their value. However, crypto works differently, namely in a cryptocurrency blockchain.
How does the cryptocurrency blockchain work?
Bitcoin exists exclusively in digital form within the computer network of all network participants, based on secure technology: the blockchain. The cryptocurrency blockchain can be quite complex but always features the following characteristics:
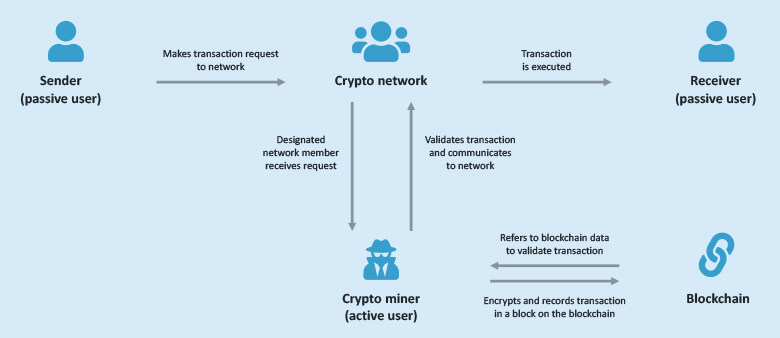
- Decentralization: A crypto blockchain is a decentralized network of computers called “nodes,” which are connected via the internet. Unlike cash, which is overseen by banks, cryptocurrencies are created and managed solely by private individuals. Administration, monitoring and transactions take place directly between private individuals or companies, which makes using a bank as an intermediary superfluous — the network is organized in a decentralized manner and regulates itself.
- Data blocks: As the name blockchain suggests, it is a chain of data blocks, because crypto transactions are carried out directly between the participants of the network. Each block in the chain contains transaction information, as well as a special record called a “hash.” A hash is a cryptographic function that ensures the integrity and uniqueness of a block. The hash of the previous block is also stored in the subsequent block, thereby creating the chain, i.e. the blockchain.
- Consensus mechanism: In order for all nodes in the blockchain to reach a consensus on which blocks to include in the chain, there are various consensus mechanisms. The best-known consensus mechanism is Proof-of-Work (PoW), in which the nodes have to solve complex mathematical problems in order to create a new block. This task is usually performed by a crypto miner. A miner is a natural person or group of natural persons and an active user of the network involved in processing transactions and securing a cryptocurrency blockchain. A passive user, on the other hand, can receive, store, and manage crypto money, but does not actively participate in the network to generate or validate transactions.
Mining crypto currencies is energy intensive and requires specialized hardware. In some cases, they can also be part of mining pools where multiple miners combine their resources. Through this process of mining, the blockchain is securely protected from tampering. This means that once in the blockchain, data is virtually immutable, which contributes to the security of the process. - Validation: Along with the consensus mechanism comes validation. The nodes of the network not only create new blocks in the blockchain, but they also check the validity of transactions and blocks to ensure compliance with established rules. This includes verifying digital signatures, checking the availability of the corresponding cryptocurrency and complying with protocol rules.
- Transaction confirmation: Once a block is created and validated, it is added to the blockchain and permanently stored throughout the blockchain. This creates an immutable and transparent record of all transactions that have ever taken place in the blockchain.
Integration possibilities for crypto blockchains
Blockchain technology offers a wide range of integration options for crypto currencies because the technology is constantly evolving, which creates new opportunities in a wide range of use cases. It is important to note that implementing blockchain integrations requires technical expertise and should take into account specific use case requirements. Currently, the most common blockchain integration opportunities are in the financial services sector.
- Payment integration: Companies can use blockchain to accept digital money as a means of payment. Through payment gateway integration, customers can use crypto currencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum to pay for goods and services. A payment gateway is a system that allows businesses to accept electronic payments from customers. It serves as an interface between the merchant, the customer and the financial institutions that process payment transactions. The payment gateway performs the task of transmitting payment data securely and efficiently and authorizing transactions in real time, while ensuring the secure processing of payments and protecting customers’ confidential information.The integration of crypto currencies as a means of payment based on a crypto blockchain is dependent upon the respective payment gateway providers. Therefore, it‘s important to consider the volatility of crypto currencies and to implement suitable mechanisms for conversion into traditional currencies, if desired.
- Wallet integration: Users can store crypto money in their digital wallets. By integrating wallet functions into apps or platforms, users can receive, send and store crypto currencies in different types of wallets, including software, hardware and online wallets. When integrating a wallet into an application or platform, there are some basic steps to consider, from wallet creation, wallet connection and transaction execution, to implementing additional security measures. Depending on the type of wallet, the application or integration platform requirements may vary. It is advisable to familiarize yourself with the specific technical documentation provided by the wallet provider or the blockchain network used to ensure a smooth integration. The wallet provider may provide APIs or SDKs to facilitate integration with the desired application.
- Smart contracts: Smart contracts are programmed specifically for the blockchain and include conditions and rules that are automatically implemented once predefined criteria are met. For example, a smart contract can automatically release payments when certain delivery conditions are met. Financial service providers can therefore use smart contracts to automate business processes and increase efficiency. Due to their automated nature and lack of human intervention, smart contracts need to be carefully developed and tested to avoid potential security vulnerabilities. Smart contracts are commonly used on the Ethereum platform to trigger payments, but other blockchain platforms such as EOS, Cardano and Tezos also support the implementation of smart contracts.
- Decentralized applications (DApps): These applications run on the decentralized crypto network based on blockchain technology. Unlike traditional centralized applications, in which data and transactions are handled by a central server, DApps use the blockchain as a transparent and trusted database. In the field of crypto currencies, the term DApps usually refers to applications developed on public blockchains such as Ethereum, EOS or Cardano. DApps are applied in various fields, including finance. Compared to traditional financial applications, DApps are usually operated without intermediaries and rely on smart contracts to enable the automated execution of financial transactions. DApps are commonly used in the financial services industry for lending platforms, decentralized exchanges and asset tokenization.
How can SEEBURGER help?
SEEBURGER has over 35 years of experience in integrating data and technologies. Our SEEBURGER BIS Platform is an agile and scalable integration platform that can connect to one or more blockchains via APIs, as well as to multiple blockchain-enabled platforms. BIS can map, convert and generate data required to participate in the blockchain, as well as manage and send data to a blockchain that has come via an adapter or from digital twins. With BIS, it’s even possible to integrate a Peppol access point into the peer or have a blockchain peer automatically store off-chain data in a data lake like HDFS and reference the hash values from the blockchain.
We use Hyperledger Fabric 2 to set up private blockchains. This software can manage multiple blockchains and also enables data outside the blockchain. An organization starts a fully functional blockchain by defining the first peer, and other peers can join as needed. Marketplaces, maintenance portals, delivery networks, platforms or web applications can be built on blockchain to support a growing number of trading partners and use cases. You can also integrate peer nodes with other blockchain-enabled platforms such as Tradelens or WeTrade to collaborate with banks and supply chain ecosystems.
Blockchain is already proving to be a gamechanger for our personal and business lives. SEEBURGER can help you drive the digital transformation of your business by leveraging our three core competencies — technology, business and experience. Contact us to learn more about how we can help you stay ahead of the curve and lay the groundwork for future growth.
Thank you for your message
We appreciate your interest in SEEBURGER
Get in contact with us:
Please enter details about your project in the message section so we can direct your inquiry to the right consultant.
Written by: Sandrine Wagner
Sandrine joined our marketing team in August 2021 as an editor and campaign manager. She holds a Bachelor's degree in International Business and brings fundamental expertise in FSI and FinTech to our marketing team through her network engagements, previous internships and student jobs. After her internship at SEEBURGER, she joined our editorial team full-time and has since been involved in writing creative and technical content for our blog and other resources in German and English. Her campaign management work focuses on trends and innovations in various sectors, most notably the financial industry. In her free time, Sandrine enjoys exploring nature with her pets, learning foreign languages and reading literature.